If you’re looking for the best heat exchanger for your business plant, plant, or system you require solid information and straightforward tips to make an informed decision. The right equipment can help you reduce energy costs, save money consumption, and ensure that your operations run smoothly.
This article will teach you the purpose of heat exchangers they do, the major kinds, how they function with the key features to look for as well as the real applications in industry, and the best way to select the best one for your requirements.
What Is a Heat Exchanger?
Heat exchangers are found all over the place from cooling towers in large factories to the air conditioning systems of buildings. The primary purpose of heat exchangers is to help systems function using less energy. They absorb the heat of a hot liquid and transfer it to an ice-cold one. This process reduces energy loss and ensures stability of systems.
Why Heat Exchangers Are Important
Heat exchangers can guide better to run system efficiently. They reduce fuel or power use. They make temperature control easier. They act as the heart of many industrial and commercial setups.
In simple terms, they help heat move where it is needed. This saves money and extends machine life. They are key to systems in many industries.
Main Types of Heat Exchangers
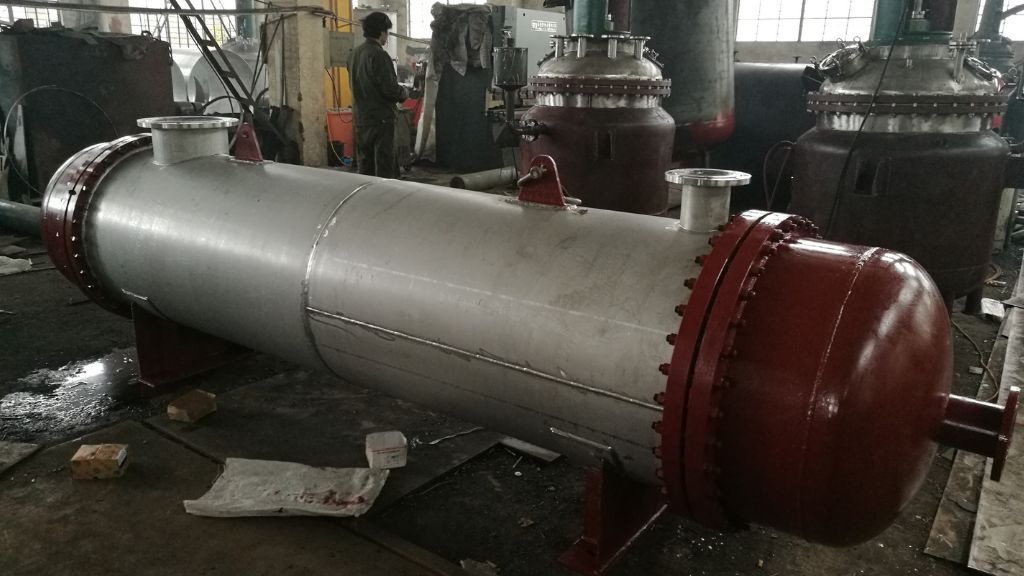
Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchanger
One fluid flows inside the tubes. Another fluid flows outside the tubes in the shell space. This setup works well with high pressure and heat loads. It is common in oil, gas, and power plants.
Pros:
- Strong build
- Good for heavy duty systems
Cons:
- Takes more space
- Harder to clean
Plate Heat Exchanger
Pros:
- High heat transfer
- Easy to clean
Cons:
- Limited pressure use
Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger
Pros:
- No water needed
- Lower water cost
Cons:
- Depends on air temp
Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
Fluids flow in different paths and exchange heat. It is common in small systems and labs.
Pros:
- Easy to make
- Low cost
Cons:
- Lower heat transfer
Key Features to Look For
1. Heat Transfer Ability
A good exchanger moves heat fast and with low energy waste. The design and surface area matter.
2. Strength and Life
The unit must resist pressure and heat for long use. Heavy use environments need tough units.
3. Easy Access and Upkeep
Look for units that can be opened for cleaning and checking without trouble.
4. Space Use
Some designs need less space. This is key in tight installations.
5. Cost Over Time
The cheapest model upfront may cost more later. Think about energy saved and maintenance needs.
How Heat Exchangers Are Used
Heat exchangers play a role in many industries. Their use is simple but very wide.
HVAC and Building Comfort
Heat exchangers transfer heat from cool or warm air. This aids in cooling and heating in offices and homes.
Refrigeration
They help change liquids to gas and back for cooling systems. This keeps products at the right temperature.
How to Choose the Right Heat Exchanger
- Check fluid type: Some fluids are hard on certain materials.
- Match pressure needs: High pressure needs strong design.
- Plan for upkeep: Can you clean and check it easily?
- Think long term: Calculate energy savings and life cost.
Heat Exchanger Comparison Table
| Type | Best Use Case | Space Use | Heat Transfer | Cleaning |
| Shell and Tube | Heavy duty plants | Large | Good | Hard |
| Plate | HVAC & food | Small | High | Easy |
| Air-Cooled | Remote sites | Medium | Moderate | Medium |
| Double Pipe | Small systems | Small | Low | Easy |
Conclusion
Heat exchangers are a crucial component in a variety of systems. They assist in transferring heat from one location to the next in a controlled manner. The ideal heat exchanger for your needs is based on your requirements space, the size of the unit and the way you intend to make use of it. Choose a product that has a excellent heat transfer, a sturdy construction, and simple maintenance to save money and improve performance.