The Church of the Highlands has recently become one of the most talked-about religious entities, not just for its massive congregations and expansive outreach programs but also due to various controversies and criticisms it has faced. This article aims to delve deep into the inner workings and the numerous aspects that have led to such public scrutiny.
Background of Church of the Highlands
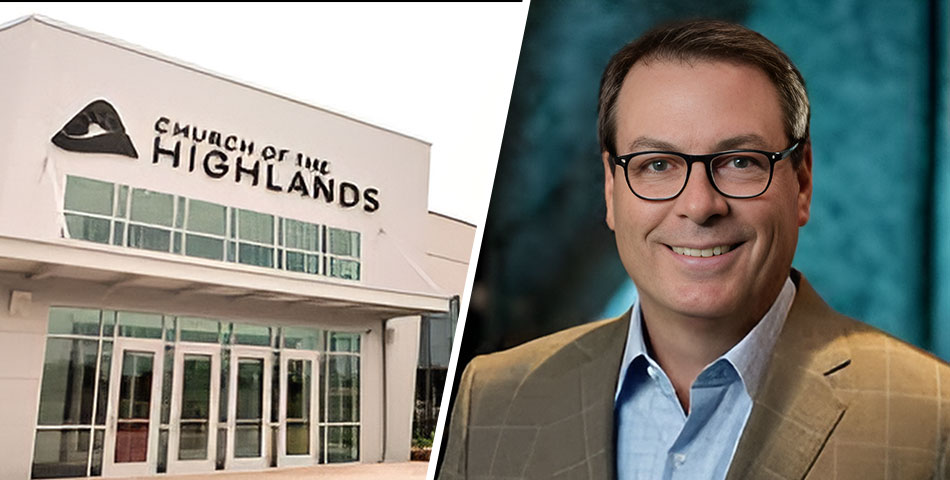
Founded in 2001 by Pastor Chris Hodges in Birmingham, Alabama, the Church of the Highlands quickly grew to become one of the largest churches in the United States. With its non-denominational approach, the church focuses on a contemporary, charismatic style of worship and a wide range of community services. As of today, it boasts multiple campuses across Alabama and conducts numerous services each Sunday that attract thousands of attendees from diverse backgrounds.
Growth and Expansion
The rapid expansion of the Church of the Highlands is noteworthy. From its humble beginnings in a high school auditorium, the church now operates over 20 campuses and several more affiliate churches. This growth can be attributed to its modern approach to worship and community engagement, which includes high-quality live broadcasts of services and strategic placement of campuses to reach more congregants. Additionally, its focus on small groups for personal spiritual development and community building has resonated well with its followers.

Financial Transparency and Criticism
One of the primary areas where the Church of the Highlands has been exposed to criticism involves its financial operations. As with many mega-churches, the vast inflows of money and how they are managed remain a focal point of debate. Critics argue that there is a lack of transparency concerning financial dealings and the compensation of its senior leaders. The church, however, maintains that it adheres to strict financial integrity and is accountable to its members and a board of overseers who audit financial transactions regularly.
Social and Political Involvement
Another dimension often puts the Church of the Highlands in the spotlight is its involvement in social and political issues. Pastor Chris Hodges’s endorsement of certain political figures and policies has led to divisive opinions among the church’s followers and the wider community. This was highlighted when the pastor liked social media posts of controversial political personalities, which stirred significant public backlash and led to some groups severing ties with the church.
Community Services and Outreach Programs
Despite the controversies, the Church of the Highlands has extensive community services and outreach programs. These include re-entry programs for prisoners, addiction recovery programs, and various charitable activities aimed at helping the underprivileged. The church’s response to natural disasters and health services, like providing COVID-19 testing sites across its campuses, exemplify its commitment to societal welfare.

Allegations and Scandals
No examination of the church would be complete without addressing the various allegations and scandals that have surfaced over the years. These include claims of racial insensitivity, mismanagement, and creating a culture where dissent is not welcomed. Such allegations have led to internal audits and reviews, with the church often having to publicly defend its practices and policies.
Spiritual Impact and Criticisms
The spiritual teachings and practices of the Church of the Highlands have also been a subject of debate. Some ex-members and critics claim that the church promotes prosperity theology, often criticized for emphasizing material success as an indication of divine favor. Additionally, some have described the church’s approach to leadership and accountability as authoritarian, with excessive control over the personal lives of its members.
Conclusion
The Church of the Highlands is a monument to modern American evangelicalism, marked by rapid growth and significant influence. However, it is also a case study ofof the complexities and challenges of such prominence. For those looking at the Church of the Highlands, whether as potential members or curious onlookers, it is crucial to consider both the accomplishments and the controversies.
In essence, the Church of the Highlands embodies the paradox of mega-churches — institutions that are capable of immense good and notable flaws. As it continues to navigate its path forward, it remains to be seen how it will address these issues and adapt to the changing landscape of American religious life.